Component: Control (DSP)
| Author | Matrix Ltd |
| Version | 1.2 |
| Category | DSP |
Contents
 Control component
Control component
Allows for several types of control operations to be performed on a buffer. On/Off - Standard on off control as used on most overs, toasters, irons. P/PI/PID - Mathematical control process to get to the setpoint as fast as possible, similar to the process in the human brain when steering a car.
Examples
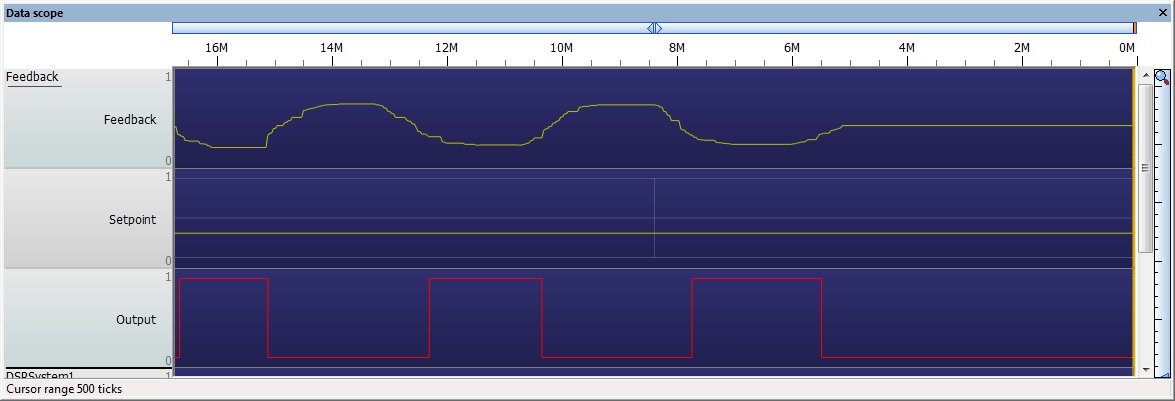
On/Off Control
Here is a basic example demonstrating on/off control.
If the Setpoint ADC is higher then the Feedback ADC plus the hysteresis value then the output will switch on.
If the Setpoint ADC is lower then the Feedback ADC then the output will switch off.
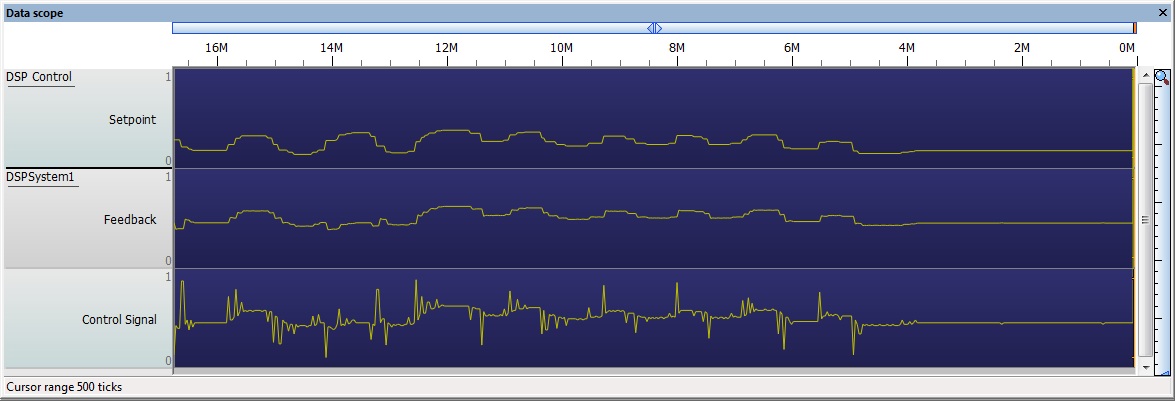
Proportional Control
Here is a basic example demonstrating proportional control.
P control is a very basic form of control which is often used as the calculations are fairly simple.
Error = (Setpoint - Feedback) Control Signal = P * Error
One major drawback of P control is that you will often get an offset between the Setpoint and the Feedback which cannot be removed due to the nature of the second or third order system.
As the setpoint potentiometer is altered the control signal tries to move the feedback to the correct position as fast as possible by creating a spike in the control signal which is equal to the amount of difference between the setpoint and the feedback readings multiplied by the P coefficient.
We have created demo 2nd and 3rd order macros to try and simulate the response of a 2nd and 3rd order system.
Here is an example of the 2nd order P control system with a P value of 4.5.
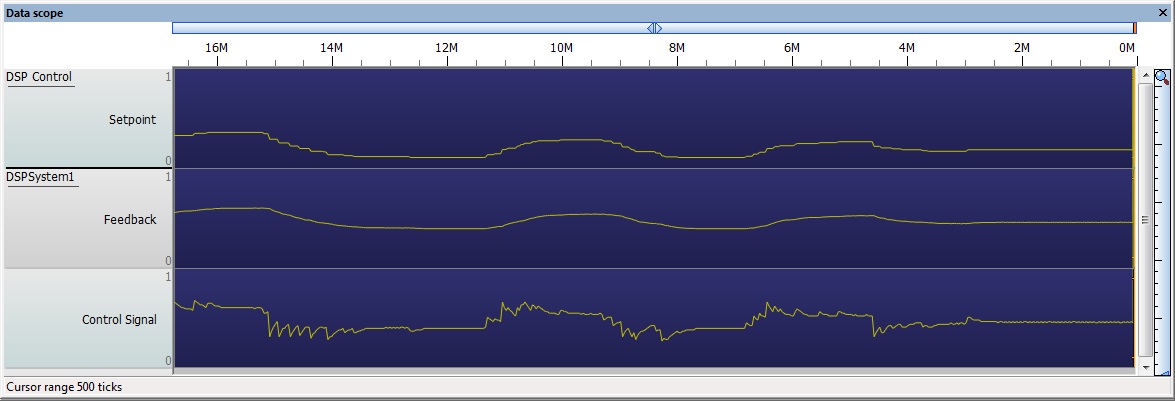
Here is an example of the 3nd order P control system with a P value of 4.5.
Proportional & Integral Control
Here is a basic example demonstrating proportional and integral control.
PI control is a slightly more advanced form of control which is often used to improve on the response of the standard P controller.
Error = (Setpoint - Feedback) Control Signal = P * (Error - Prev Error + (Error / I))
One major upside of PI control is that it will work to reduce the offset between the setpoint and the actual value. One drawback of this is that a badly tuned PI controller will be very unstable due to an effect called integral wind up.
Here is an example of the 2nd order PI control system with a P value of 4.5 and an I value of 2.5.
Here is an example of the 3nd order PI control system with a P value of 4.5 and an I value of 2.5.
Here is an example of the 2nd order PI control system with badly tuned P and I coefficients.
Downloadable macro reference
Process
Processes an entire buffer, either by performing the control operation to every value in the buffer or just the last value.
Parameters
- INT Setpoint
- Value to specify the required control setpoint
Return value
- This call does not return a value
ProcessTick
Processes the current value from a buffer.
Parameters
- INT Setpoint
- Value to specify the required control setpoint
Return value
- This call does not return a value
Simulation macro reference
This component does not contain any simulation macros
Property reference
Buffer Manager
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name buffer_manager.
DSP buffer manager to get the buffers from
Feedback
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name input_a.
Feedback buffer - used to pass the feedback reading into the control algorythm.
Output
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name output_c.
Output buffer - used to pass the control output values from the control algorythm.
Process
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name style.
Selects whether to process the entire buffer or just a single value when calling the Process macro
Method
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name method.
Specifies which control method will be used to process the buffer data
Proportional
This property is of type Signed integer and can be referenced with the variable name proportional.
P coefficient used to perform the Proportional calculation
Integral
This property is of type Signed integer and can be referenced with the variable name integral.
I coefficient used to perform the Integral calculation
Derivative
This property is of type Signed integer and can be referenced with the variable name derivative.
D coefficient used to perform the Derivative calculation