Difference between revisions of "Component: UART (RS232) (Comms: Interface)"
(XML import BR) |
(XML import) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
On a microcontroller the interface will be the onboard UART which will need voltage level shifting using a max2323 to become RS232 compatible. | On a microcontroller the interface will be the onboard UART which will need voltage level shifting using a max2323 to become RS232 compatible. | ||
See the EB015 RS232 E-block for details. | See the EB015 RS232 E-block for details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Detailed description== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Overview=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The RS232 component is in fact nothing more than a TTL level asynchronous serial communications bus which basically means that there is no clock signal. Instead the data is sent out at a precise data rate specified by the Baud which is represented in bits per second. Both devices need to be set to the same rate to allow communications to work correctly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
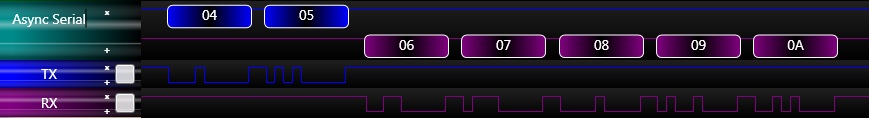
| + | There are two signals which make up the asynchronous serial connection: RX and TX. The receive RX signal is used for incoming data and the transmit TX signal is used for outgoing data. When connecting two devices together it is important to connect the TX of one device to the RX of the other and visa versa. When inactive the bus defaults to having the TX signal held in the high state. Each data byte sent then starts with a low signal for 1 period of the baud rate to signify that data is to follow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Each RS232 transaction consists of a byte made up of 8 clock cycles allowing the 8-bits of the byte to be transferred. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RS232_Bytes.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===TTL=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | By default the RS232 component will provide TTL asynchronous serial data which is best suited for a single device to single device data connection on the same circuit board. An example might be a GSM modem or GPS module. The TTL signals are normally at VCC when the bus is idle and toggles between VCC and Ground when sending data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===RS232=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | By adding a driver chip such as a MAX2323 the TTL signals can be upgraded to RS232 which is best suited for single device to single device mid range off board communications. The RS232 signals replace the voltages VCC with +12V and GND with -12V to allow for better noise rejection in noisy environments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===RS485=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | By adding a driver chip such as a MAX3078 the TTL signals can be upgraded to RS485 which is best suited for master to multiple slave type mid range off board communications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Auto Baud=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some devices feature an auto baud functionality and is commonly triggered by sending a known data byte to the device before any other data is sent allowing the correct baud to be worked out. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Importing from v5=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The RS232 component in Flowcode v6 has a new Initialise macro which will need to be added to your program before any other calls to the component are made. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| − | + | ===Transmit=== | |
| + | |||
| + | This example transmits a string "Hello World". | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|RS232_Example1.fcfx|RS232_Example1}} | ||
| + | The Console window shows the data as it is sent and received. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RS2321.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Receive=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This example receives a character and outputs it to the LCD, an injector has been added to allow you to type data into the console. | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|RS232_Example2.fcfx|RS232_Example2}} | ||
| + | The Console window has tabs for the human interface data injector allowing you to type in data that will be received by the component. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RS2322.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Again the RS232 console tabs reflect the data as it is sent and received. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RS2323.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | LCD showing received data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RS2324.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Transmit and Receive=== | ||
| + | This example echoes back any data that is received allowing a nice sanity check when connecting an embedded device to a PC or other source of communications. | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|RS232_Example3.fcfx|RS232_Example3}} | ||
| + | Again the RS232 console tabs reflect the data as it is sent and received. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RS2325.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===UART Bridge=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This example allows a microcontroller with two UART peripherals to receive data one one UART and transmit on the other and visa versa in a reliable manner using interrupts. Note that this method will only work with hardware UART channels. A software UART could be done in a similar way using a falling edge type interrupt on the UART RX pin to trigger the receive function. | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|UART_Bridge.fcfx|RS232_Example4}} | ||
| + | ===COM Port=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The COM port property allows you to attach the RS232 component to a COM port on your PC during simulation allowing real world hardware such as RS232, Bluetooth, GPS to work with the simulation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Injector=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Injector property allows you to select an injector component on the panel for use in the simulation. The human interface injector can be used to inject typed in data via the console window and can be seen in examples 2 and 3 above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are other pre-made injectors to allow you to do various aspects from simulating a generic AT terminal to simulating a specific remote device. | ||
==Downloadable macro reference== | ==Downloadable macro reference== | ||
| Line 87: | Line 175: | ||
:[[Variable Types|BYTE]] ''Timeout'' | :[[Variable Types|BYTE]] ''Timeout'' | ||
| + | ::Time to wait in milliseconds for valid data before returning, 0=Dont wait, 255=Wait forever. | ||
| − | :[[Variable Types| | + | :[[Variable Types|UINT]] ''NumBytes'' |
| + | ::The number of bytes to try and receive, ideally your string variable should have at least 1 more byte to store the null termination byte | ||
| Line 115: | Line 205: | ||
:[[Variable Types|INT]] ''Timeout'' | :[[Variable Types|INT]] ''Timeout'' | ||
| − | ::Time to wait for valid data before returning, 0=Dont wait, 255=Wait forever. | + | ::Time to wait in milliseconds for valid data before returning, 0=Dont wait, 255=Wait forever. |
| Line 126: | Line 216: | ||
==Simulation macro reference== | ==Simulation macro reference== | ||
| − | + | ''This component does not contain any simulation macros'' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | ''' | + | ==Property reference== |
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Channel</u></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::CHANNEL''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | UART Channel selector | ||
| + | |||
| + | Software channels are bit banged using generic I/O pins but are not as reliable as hardware channels. | ||
| − | + | Hardware channels use the selected peripheral on-board the target microcontroller. | |
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Baud Options</u></span> | ||
| − | ''' | + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::BAUD_LIST''. |
| − | + | Baud rate option selector | |
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Baud Rate</u></span> | ||
| + | This property is of type ''Signed integer'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::BAUD''. | ||
| + | ''<span style="color:red;">No additional information</span>'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Data Bits</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::DBITS''. | |
| − | + | Number of data bits | |
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Return</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::RETURN''. | |
| − | + | Return data width from Receive macro. | |
| − | + | 8-bit data mode always returns a byte ranging from 0-255, 255 could mean a timeout or could be a valid data. | |
| − | + | 16-bit data mode rereturns 0-255 for valid data, 256 for a timeout, return data must be stored into an INT or UINT variable. | |
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Echo</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::ECHO''. | |
| − | + | Automatically echoes back any received data when enabled by re-transmitting the received byte. | |
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Use TX</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::UseTX''. | |
| − | + | Selects if the Transmit pin is used by the component. | |
| − | + | Yes: The TX pin is active and used to transmit data for the UART. | |
| − | + | No: The TX pin is disabled and free to be used as general I/O. | |
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>TX</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''Single digital pin'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::TX''. | |
| − | + | Pin to be used for Transmit data | |
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>TX Alt Pin</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::TXAlt''. | |
| − | + | Allows the TX pin to be allocated to an alternate I/O pin. | |
| − | + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Use RX</u></span> | |
| − | + | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::UseRX''. | |
| − | + | Selects if the Receive pin is used by the component. | |
| − | + | Yes: The RX pin is active and used to receive data for the UART. | |
| − | + | No: The RX pin is disabled and free to be used as general I/O. | |
<span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>RX</u></span> | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>RX</u></span> | ||
| − | This property is of type ''Single digital pin'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''RX''. | + | This property is of type ''Single digital pin'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::RX''. |
| − | + | Pin to be used for Receive data | |
| + | |||
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>RX Alt Pin</u></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::RXAlt''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Allows the RX pin to be allocated to an alternate I/O pin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Use Flow Control</u></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::FLOWEN''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Flow Control (Handshake) enable or disable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On: Two I/O pins are used to control the flow of data in and out of the device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Off: Flow control is disabled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>RTS</u></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This property is of type ''Single digital pin'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::RTS''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pin to be used for Request To Send handshake function | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output from target micro to inform remote device we are ready to receive data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Low = Ready to receive data | ||
| + | |||
| + | High = Not ready to receive data | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>CTS</u></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This property is of type ''Single digital pin'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::CTS''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pin to be used for Clear To Send handshake function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Input to target micro to inform when the remote device is ready to transmit data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Low = Ready to transmit data | ||
| + | |||
| + | High = Not ready to transmit data | ||
<span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Label</u></span> | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Label</u></span> | ||
| Line 214: | Line 352: | ||
<span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Scope Traces</u></span> | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Scope Traces</u></span> | ||
| − | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''ScopeTraces''. | + | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::ScopeTraces''. |
| + | |||
| + | Selects if the scope traces are automatically added to the data recorder window or not. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Simulation - draws an approximation of the UART data onto the scope trace. | ||
| − | + | ICT - sets up the scope trace for incoming data and adds UART packet decoding at the correct BAUD. | |
<span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Console Data</u></span> | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Console Data</u></span> | ||
| − | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''ConsoleData''. | + | This property is of type ''True or false'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::ConsoleData''. |
Selects if the console data is automatically generated or not | Selects if the console data is automatically generated or not | ||
| Line 226: | Line 368: | ||
<span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Console Columns</u></span> | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Console Columns</u></span> | ||
| − | This property is of type ''Unsigned integer'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''ConsoleColumns''. | + | This property is of type ''Unsigned integer'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::ConsoleColumns''. |
Number of characters that can be displayed on a single line of the console. | Number of characters that can be displayed on a single line of the console. | ||
| Line 232: | Line 374: | ||
<span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Data Source</u></span> | <span style="font-weight: normal;"><u>Data Source</u></span> | ||
| − | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''DataSource''. | + | This property is of type ''Fixed list of ints'' and can be referenced with the variable name ''cal_uart::DataSource''. |
| − | Simulation data source used to allow the component to connect to | + | Simulation data source used to allow the component to connect to various remote devices |
| − | + | Nothing - Simulation data is ignored | |
| − | + | COM port - Routes the communication data to and from a physical or virtual COM port | |
| − | + | Injector - Routes the communication data via a data injector component on the Panel. | |
Latest revision as of 10:31, 9 May 2018
| Author | Matrix Ltd |
| Version | 2.0 (Release) |
| Category | Comms: Interface |
Contents
 UART (RS232) component
UART (RS232) component
Low level routines for controlling or interacting with a standard asyncronous serial interface. On a microcontroller the interface will be the onboard UART which will need voltage level shifting using a max2323 to become RS232 compatible. See the EB015 RS232 E-block for details.
Detailed description
Overview
The RS232 component is in fact nothing more than a TTL level asynchronous serial communications bus which basically means that there is no clock signal. Instead the data is sent out at a precise data rate specified by the Baud which is represented in bits per second. Both devices need to be set to the same rate to allow communications to work correctly.
There are two signals which make up the asynchronous serial connection: RX and TX. The receive RX signal is used for incoming data and the transmit TX signal is used for outgoing data. When connecting two devices together it is important to connect the TX of one device to the RX of the other and visa versa. When inactive the bus defaults to having the TX signal held in the high state. Each data byte sent then starts with a low signal for 1 period of the baud rate to signify that data is to follow.
Each RS232 transaction consists of a byte made up of 8 clock cycles allowing the 8-bits of the byte to be transferred.
TTL
By default the RS232 component will provide TTL asynchronous serial data which is best suited for a single device to single device data connection on the same circuit board. An example might be a GSM modem or GPS module. The TTL signals are normally at VCC when the bus is idle and toggles between VCC and Ground when sending data.
RS232
By adding a driver chip such as a MAX2323 the TTL signals can be upgraded to RS232 which is best suited for single device to single device mid range off board communications. The RS232 signals replace the voltages VCC with +12V and GND with -12V to allow for better noise rejection in noisy environments.
RS485
By adding a driver chip such as a MAX3078 the TTL signals can be upgraded to RS485 which is best suited for master to multiple slave type mid range off board communications.
Auto Baud
Some devices feature an auto baud functionality and is commonly triggered by sending a known data byte to the device before any other data is sent allowing the correct baud to be worked out.
Importing from v5
The RS232 component in Flowcode v6 has a new Initialise macro which will need to be added to your program before any other calls to the component are made.
Examples
Transmit
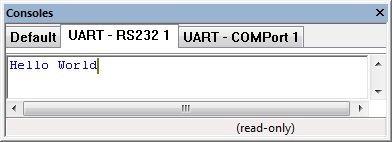
This example transmits a string "Hello World".
![]() RS232_Example1
The Console window shows the data as it is sent and received.
RS232_Example1
The Console window shows the data as it is sent and received.
Receive
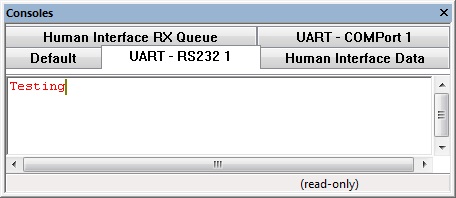
This example receives a character and outputs it to the LCD, an injector has been added to allow you to type data into the console.
![]() RS232_Example2
The Console window has tabs for the human interface data injector allowing you to type in data that will be received by the component.
RS232_Example2
The Console window has tabs for the human interface data injector allowing you to type in data that will be received by the component.
Again the RS232 console tabs reflect the data as it is sent and received.
LCD showing received data.
Transmit and Receive
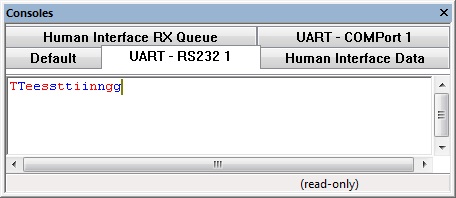
This example echoes back any data that is received allowing a nice sanity check when connecting an embedded device to a PC or other source of communications.
![]() RS232_Example3
Again the RS232 console tabs reflect the data as it is sent and received.
RS232_Example3
Again the RS232 console tabs reflect the data as it is sent and received.
UART Bridge
This example allows a microcontroller with two UART peripherals to receive data one one UART and transmit on the other and visa versa in a reliable manner using interrupts. Note that this method will only work with hardware UART channels. A software UART could be done in a similar way using a falling edge type interrupt on the UART RX pin to trigger the receive function.
![]() RS232_Example4
RS232_Example4
COM Port
The COM port property allows you to attach the RS232 component to a COM port on your PC during simulation allowing real world hardware such as RS232, Bluetooth, GPS to work with the simulation.
Injector
The Injector property allows you to select an injector component on the panel for use in the simulation. The human interface injector can be used to inject typed in data via the console window and can be seen in examples 2 and 3 above.
There are other pre-made injectors to allow you to do various aspects from simulating a generic AT terminal to simulating a specific remote device.
Downloadable macro reference
SendString
Sends out a string of bytes from the UART interface.
Parameters
- <- STRING Data
- This parameter may be returned back to the caller
Return value
- This call does not return a value
SendNumber
Sends out a number as an ASCII String from the UART interface.
Parameters
- <- LONG Number
- This parameter may be returned back to the caller
Return value
- This call does not return a value
SendChar
Sends out a single packet from the UART interface.
Parameters
- INT Char
Return value
- This call does not return a value
ChangeHWBaud
Changes the hardware UART baud rate allowing for dynamic speed changes.
Parameters
- BYTE NewBaud
- 0=1200, 1=2400, 2=4800, 3=9600, 4=19200, 5=38400, 6=57600, 7=115200
Return value
- This call does not return a value
ReceiveString
Attempts to receive a string of bytes from the UART interface.
Parameters
- BYTE Timeout
- Time to wait in milliseconds for valid data before returning, 0=Dont wait, 255=Wait forever.
- UINT NumBytes
- The number of bytes to try and receive, ideally your string variable should have at least 1 more byte to store the null termination byte
Return value
Initialise
Sets up the RS232 peripheral, must be called at the start of your program or at least before you start calling any other RS232 macros.
Parameters
- This macro has no parameters
Return value
- This call does not return a value
ReceiveChar
Attempts to receive a single packet from the UART interface.
Parameters
- INT Timeout
- Time to wait in milliseconds for valid data before returning, 0=Dont wait, 255=Wait forever.
Return value
Simulation macro reference
This component does not contain any simulation macros
Property reference
Channel
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::CHANNEL.
UART Channel selector
Software channels are bit banged using generic I/O pins but are not as reliable as hardware channels.
Hardware channels use the selected peripheral on-board the target microcontroller.
Baud Options
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::BAUD_LIST.
Baud rate option selector
Baud Rate
This property is of type Signed integer and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::BAUD.
No additional information
Data Bits
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::DBITS.
Number of data bits
Return
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::RETURN.
Return data width from Receive macro.
8-bit data mode always returns a byte ranging from 0-255, 255 could mean a timeout or could be a valid data.
16-bit data mode rereturns 0-255 for valid data, 256 for a timeout, return data must be stored into an INT or UINT variable.
Echo
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::ECHO.
Automatically echoes back any received data when enabled by re-transmitting the received byte.
Use TX
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::UseTX.
Selects if the Transmit pin is used by the component.
Yes: The TX pin is active and used to transmit data for the UART.
No: The TX pin is disabled and free to be used as general I/O.
TX
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::TX.
Pin to be used for Transmit data
TX Alt Pin
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::TXAlt.
Allows the TX pin to be allocated to an alternate I/O pin.
Use RX
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::UseRX.
Selects if the Receive pin is used by the component.
Yes: The RX pin is active and used to receive data for the UART.
No: The RX pin is disabled and free to be used as general I/O.
RX
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::RX.
Pin to be used for Receive data
RX Alt Pin
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::RXAlt.
Allows the RX pin to be allocated to an alternate I/O pin.
Use Flow Control
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::FLOWEN.
Flow Control (Handshake) enable or disable.
On: Two I/O pins are used to control the flow of data in and out of the device.
Off: Flow control is disabled.
RTS
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::RTS.
Pin to be used for Request To Send handshake function
Output from target micro to inform remote device we are ready to receive data.
Low = Ready to receive data
High = Not ready to receive data
CTS
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::CTS.
Pin to be used for Clear To Send handshake function.
Input to target micro to inform when the remote device is ready to transmit data.
Low = Ready to transmit data
High = Not ready to transmit data
Label
This property is of type Line of text and can be referenced with the variable name label.
Textual label shown on the component I/O flasher
Scope Traces
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::ScopeTraces.
Selects if the scope traces are automatically added to the data recorder window or not.
Simulation - draws an approximation of the UART data onto the scope trace.
ICT - sets up the scope trace for incoming data and adds UART packet decoding at the correct BAUD.
Console Data
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::ConsoleData.
Selects if the console data is automatically generated or not
Console Columns
This property is of type Unsigned integer and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::ConsoleColumns.
Number of characters that can be displayed on a single line of the console.
Data Source
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name cal_uart::DataSource.
Simulation data source used to allow the component to connect to various remote devices
Nothing - Simulation data is ignored
COM port - Routes the communication data to and from a physical or virtual COM port
Injector - Routes the communication data via a data injector component on the Panel.